Author: Zahra Hassan
We are currently navigating an era of unprecedented technological transformation known as Industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This shift represents more than just a new set of tools; it is a fundamental reconfiguration of work in the digital age that bridges the physical, digital, and biological worlds. For business owners, this revolution offers a path to become more efficient, agile, and competitive in a rapidly evolving global market.
What is Industry 4.0?
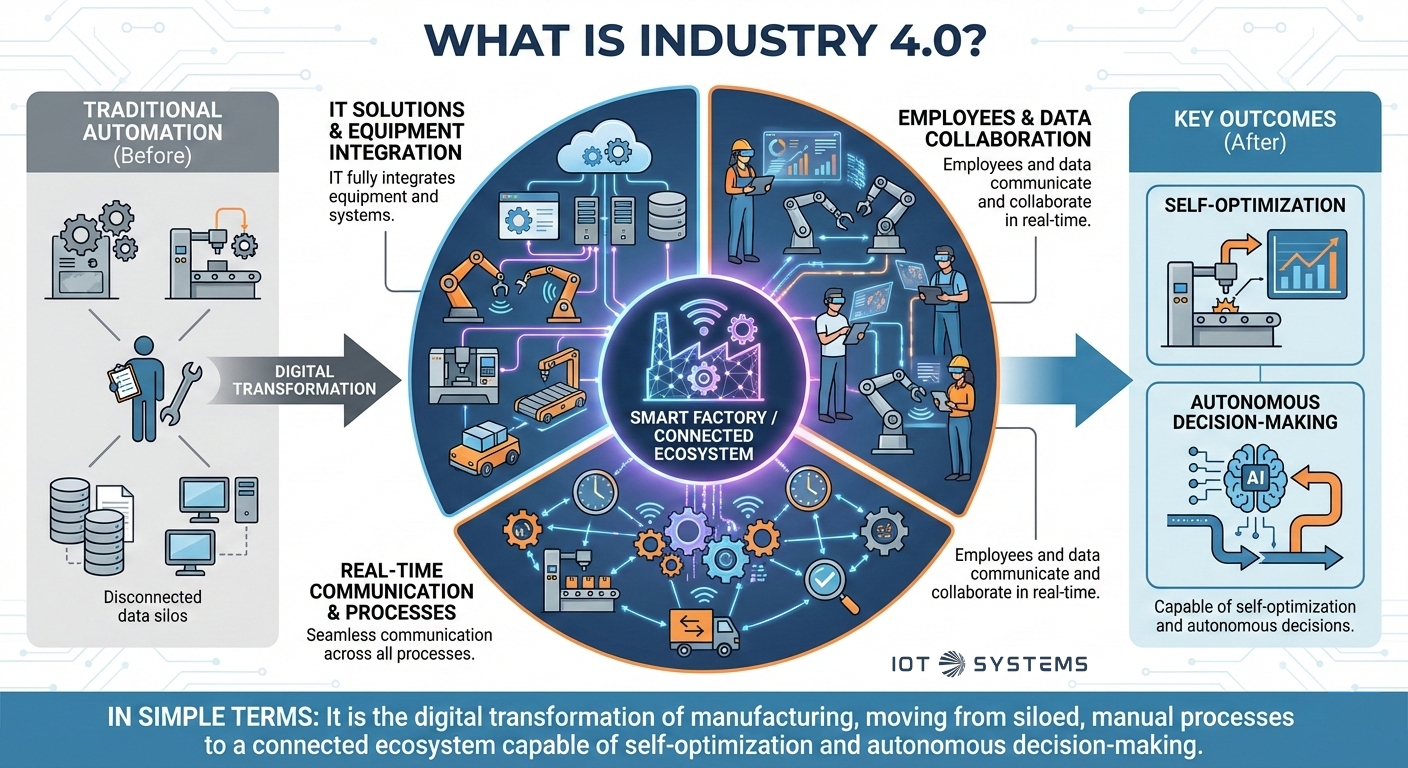
Industry 4.0 refers to the intelligent networking of production systems where information technology (IT) solutions fully integrate equipment, employees, and data. Unlike traditional automation, it focuses on creating smart factories where machines, people, and processes communicate and collaborate seamlessly in real-time.
In simple terms, it is the digital transformation of manufacturing, moving from siloed, manual processes to a connected ecosystem capable of self-optimization and autonomous decision-making.
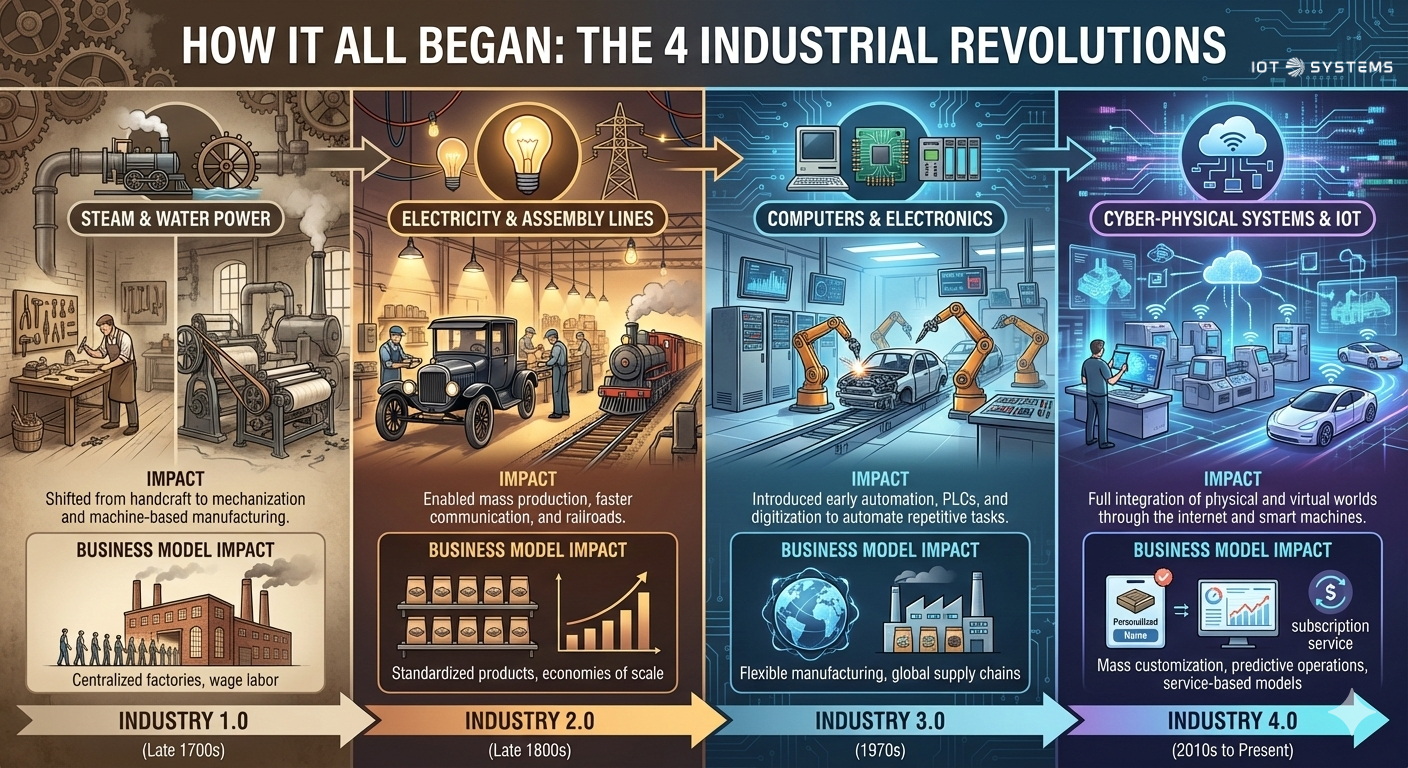
How It All Began: The 4 Industrial Revolutions
The history of industrial progress is marked by four distinct periods of monumental change:
The Foundation of Industry 4.0: Hyperconnectivity
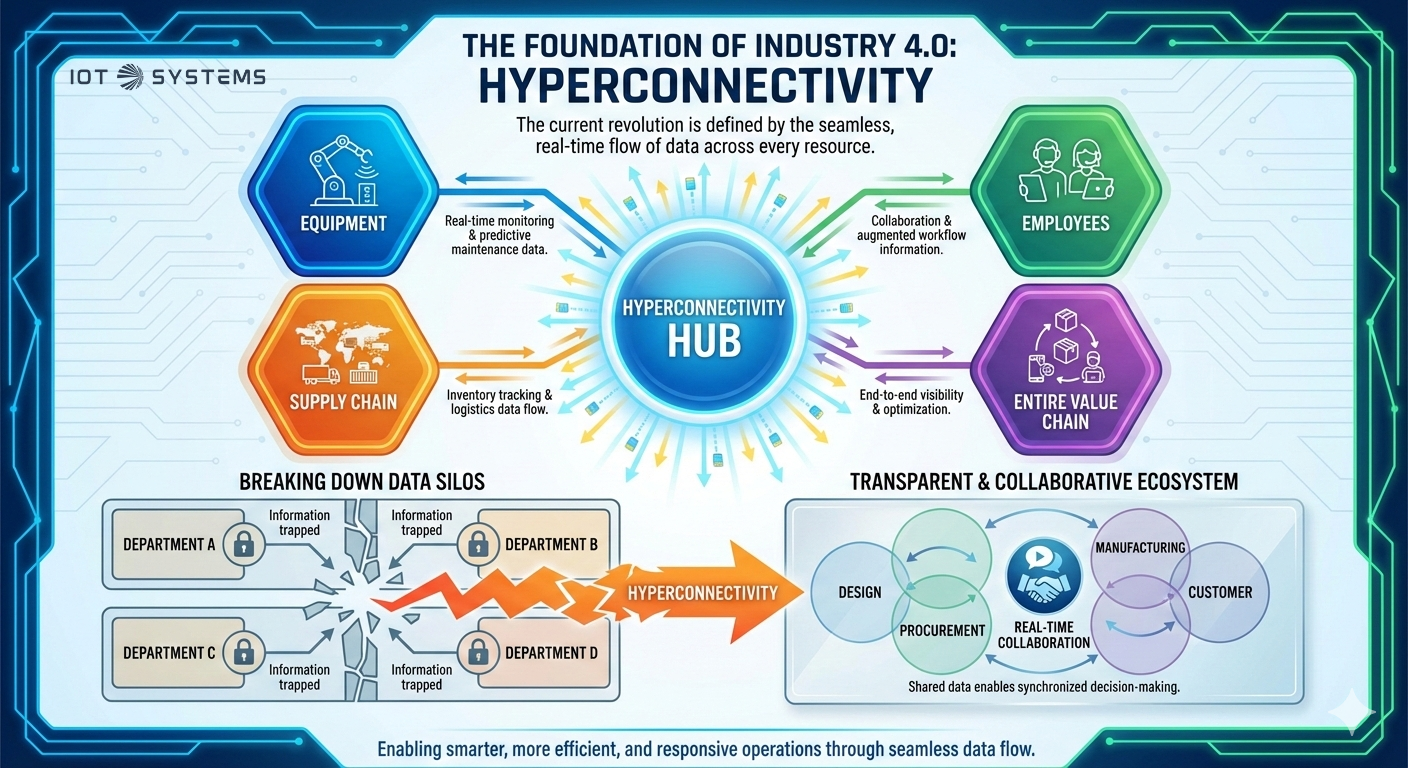
What truly sets the current revolution apart is hyperconnectivity. This is the smooth, real-time flow of data across every resource: equipment, employees, and the supply chain. By breaking down data silos where information is trapped in specific departments, hyperconnectivity allows data to flow smoothly across the entire value chain. This makes a company’s resources transparent, allowing for real-time collaboration between design, procurement, manufacturing, and the customer.
The Impact: Revolutionizing Manufacturing
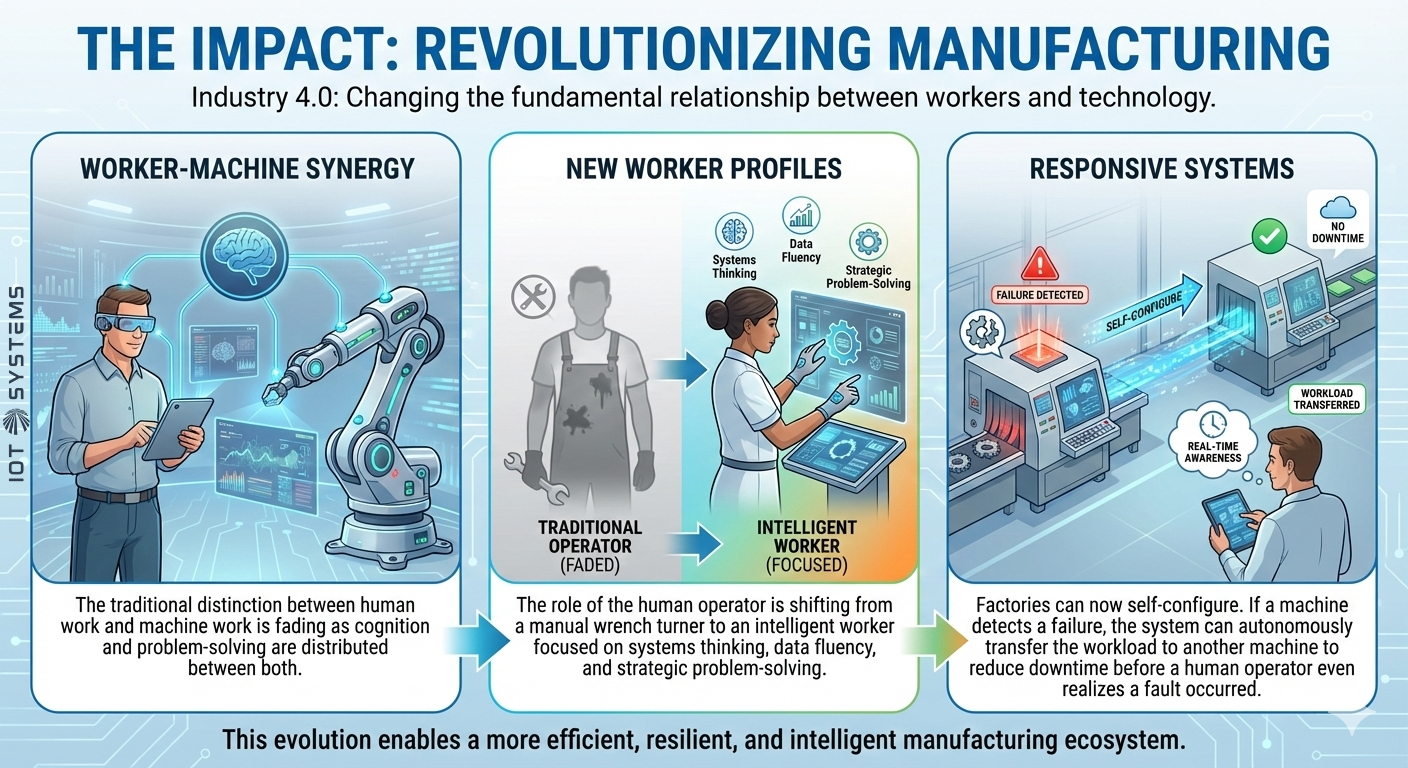
Industry 4.0 isn’t just about faster machines; it’s about changing the fundamental relationship between workers and technology.
• Worker-Machine Synergy: The traditional distinction between human work and machine work is fading as cognition and problem-solving are distributed between both.
• New Worker Profiles: The role of the human operator is shifting from a manual wrench turner to an intelligent worker focused on systems thinking, data fluency, and strategic problem-solving.
• Responsive Systems: Factories can now self-configure. If a machine detects a failure, the system can autonomously transfer the workload to another machine to reduce downtime before a human operator even realizes a fault occurred.
Core Technologies Behind Industry 4.0
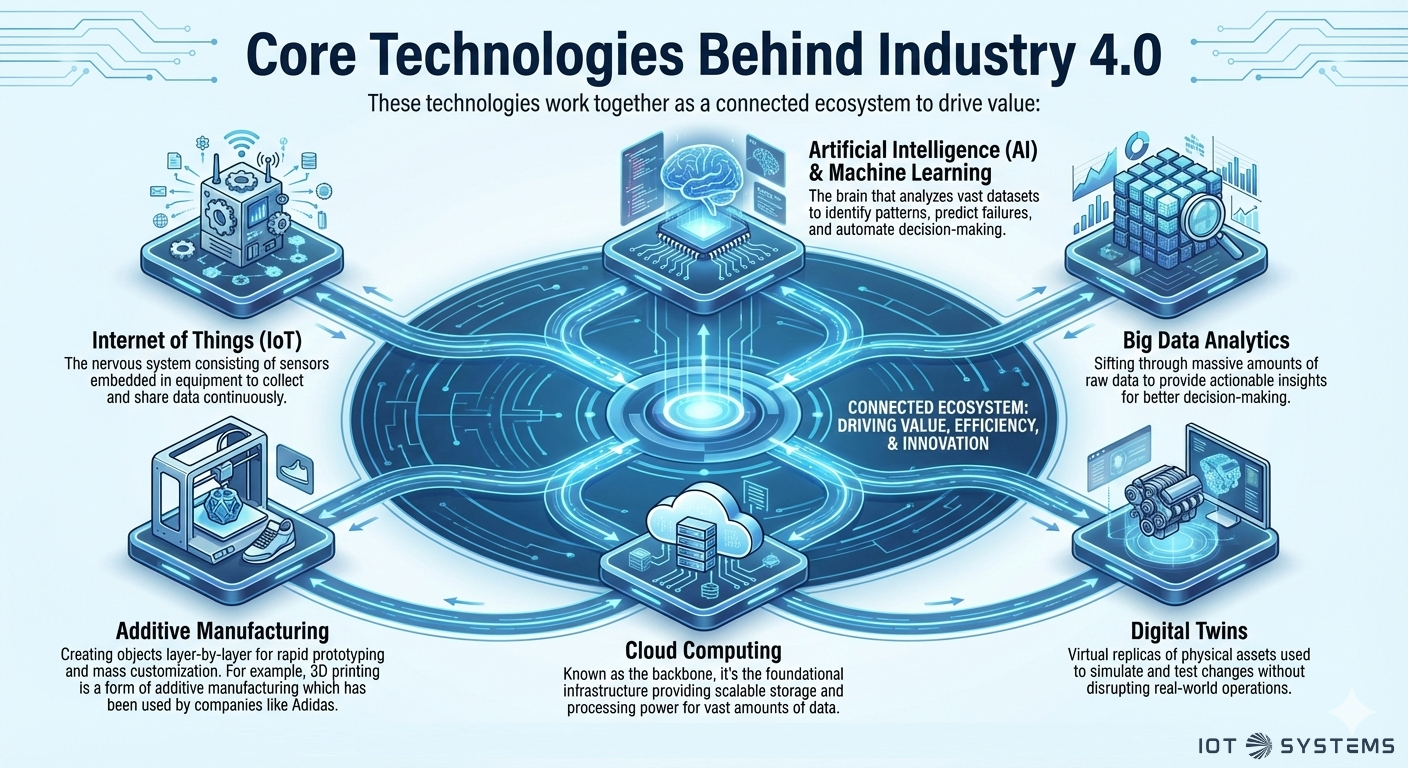
These technologies work together as a connected ecosystem to drive value:
• Internet of Things (IoT): The nervous system consisting of sensors embedded in equipment to collect and share data continuously.
• Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning: The brain that analyzes vast datasets to identify patterns, predict failures, and automate decision-making.
• Big Data Analytics: Sifting through massive amounts of raw data to provide actionable insights for better decision-making.
• Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical assets used to simulate and test changes without disrupting real-world operations.
• Cloud Computing: Known as the backbone, it’s the foundational infrastructure providing scalable storage and processing power for vast amounts of data.
• Additive Manufacturing: Creating objects layer-by-layer for rapid prototyping and mass customization. For example, 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing which has been used by companies like Adidas.
How These Technologies Work Together: A Real-World Example
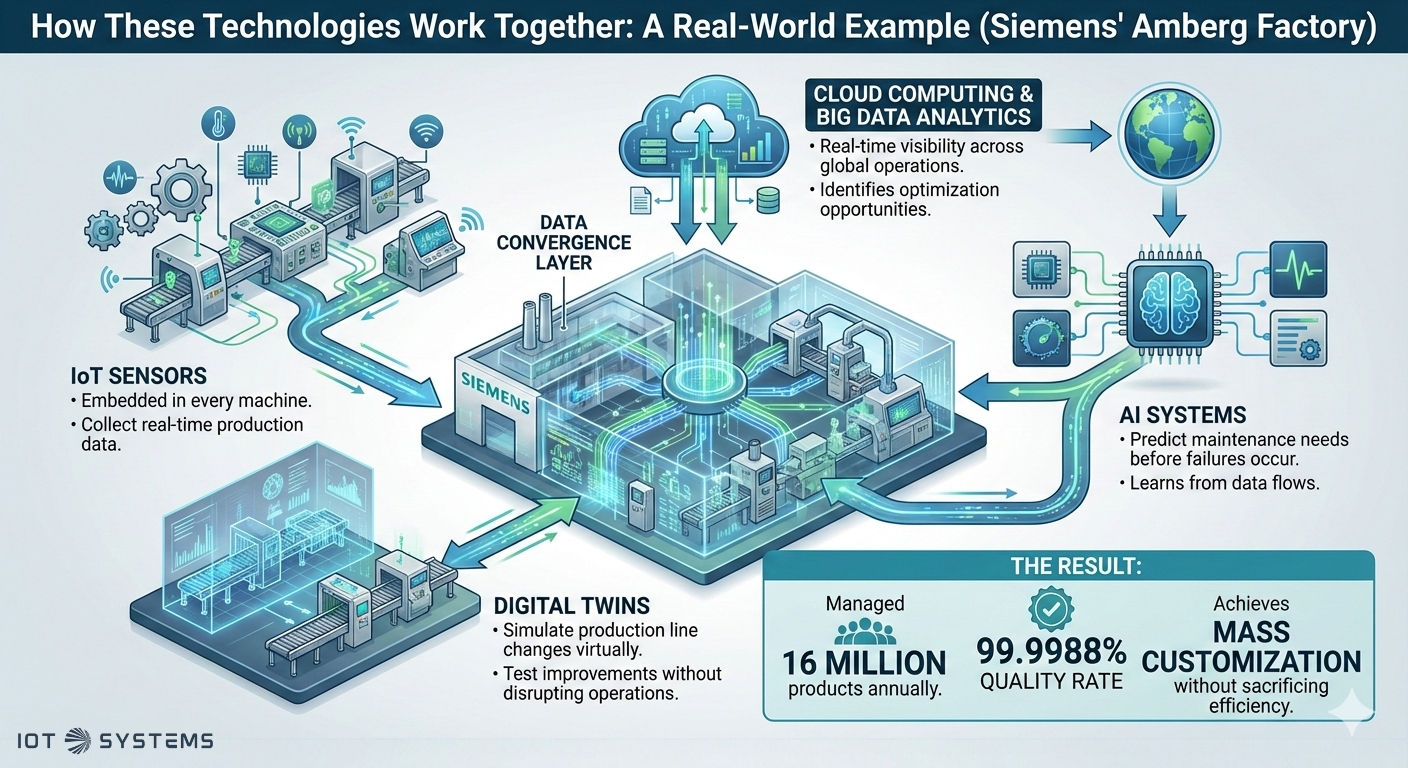
Siemens’ Amberg factory in Germany demonstrates how these technologies converge into a seamless system:
- IoT sensors embedded in every machine collect real-time production data.
- This data flows into AI systems that predict maintenance needs before failures occur.
- Digital twins simulate production line changes virtually, allowing engineers to test improvements without disrupting actual operations.
- Cloud computing enables real-time visibility across global operations, while big data analytics identifies optimization opportunities.
The result? The factory manages 16 million products annually with a 99.9988% quality rate, achieving mass customization without sacrificing efficiency. This integration of technologies working in concert, not in isolation, is what makes Industry 4.0 transformative.
Four Design Principles of Industry 4.0
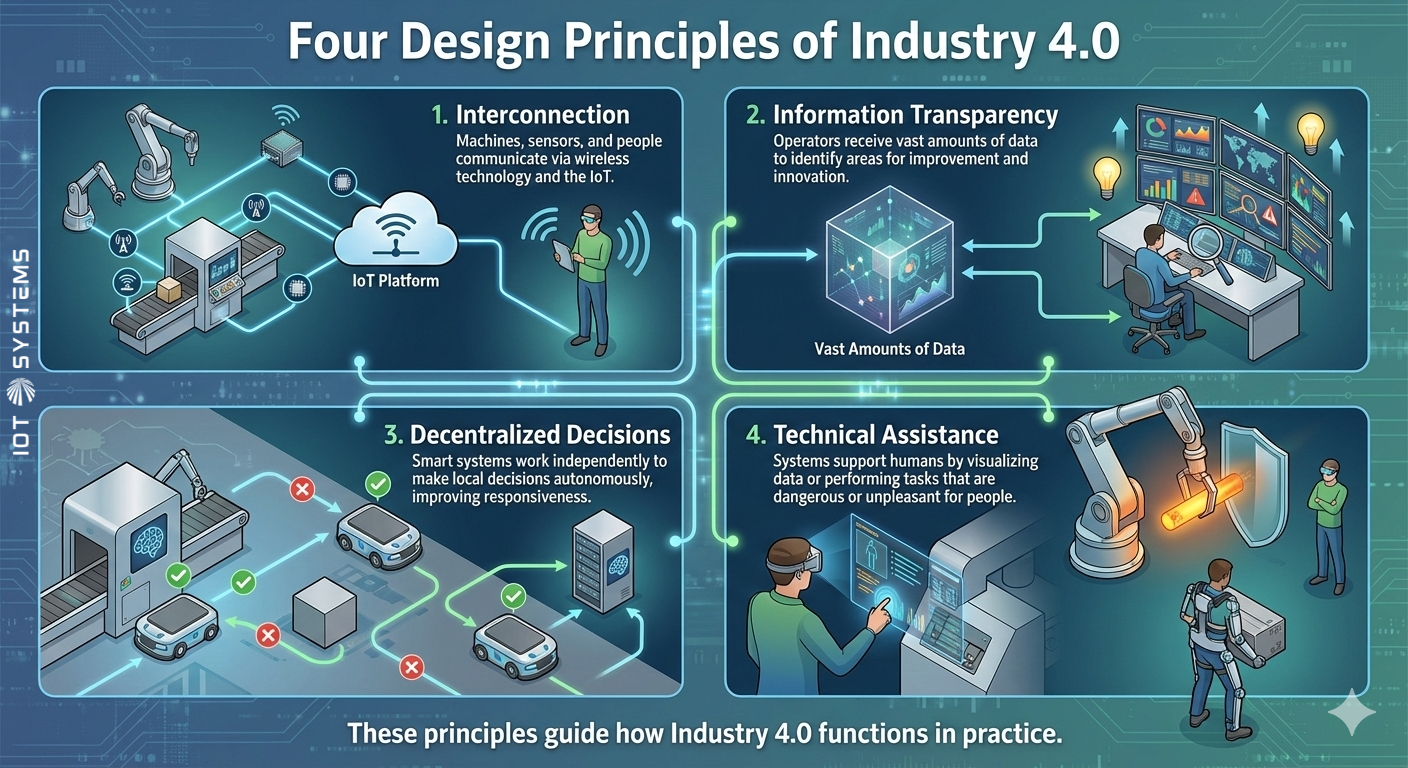
These principles guide how Industry 4.0 functions in practice:
1. Interconnection: Machines, sensors, and people communicate via wireless technology and the IoT.
2. Information Transparency: Operators receive vast amounts of data to identify areas for improvement and innovation.
3. Decentralized Decisions: Smart systems work independently to make local decisions autonomously, improving responsiveness.
4. Technical Assistance: Systems support humans by visualizing data or performing tasks that are dangerous or unpleasant for people.
IoT and Industry 4.0
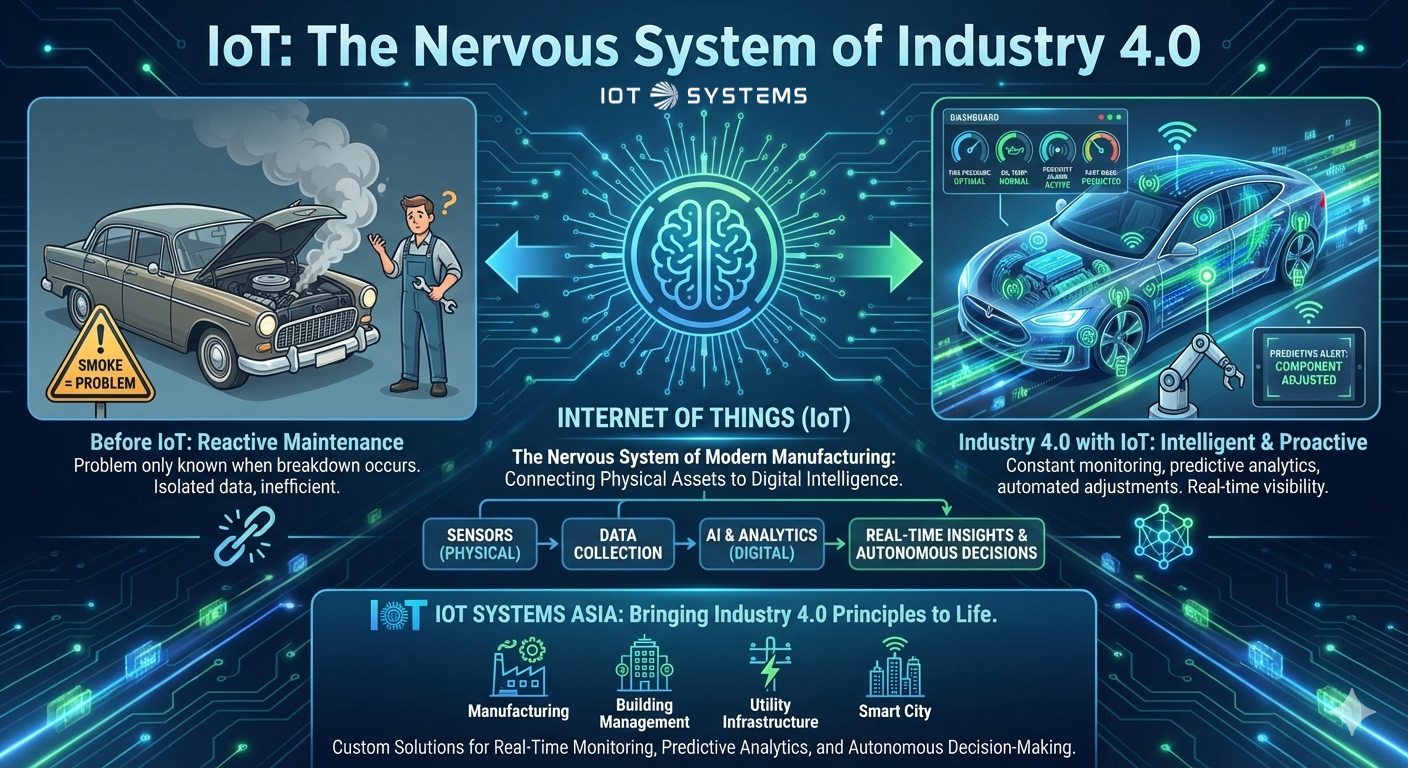
In the context of Industry 4.0, the Internet of Things (IoT) functions as the nervous system of modern manufacturing, providing the essential link between physical production and digital intelligence. This technology involves a massive network of industrial devices, often referred to specifically as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) that are equipped with sensors to collect, analyze, and exchange data in real-time.
IoT gives manufacturers “eyes everywhere” on the factory floor. By embedding smart sensors into machinery, businesses gain full visibility into asset health, production statuses, and environmental parameters. This eliminates data silos and ensures that information flows smoothly across different departments, from design to customer service.
Imagine your factory as a high-end modern vehicle. In older cars, you only knew there was a problem when smoke came out of the engine. In a connected Industry 4.0 factory, the IoT sensors are like the car’s internal computer system that constantly monitors tire pressure, oil temperature, and proximity to other cars. It doesn’t just wait for a breakdown; it tells you exactly which part is wearing out and can even automatically adjust the braking or engine performance to keep you safe and efficient before you even notice a vibration in the steering wheel.
At IOT Systems Asia, we develop custom IoT software solutions that bring Industry 4.0 principles to life across multiple sectors. Whether you’re modernizing manufacturing operations, optimizing building management systems, enhancing utility infrastructure, or building smart city capabilities, our tailored solutions connect your physical assets to intelligent software platforms that enable real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and autonomous decision-making.
How Businesses Benefit (and the ROI)
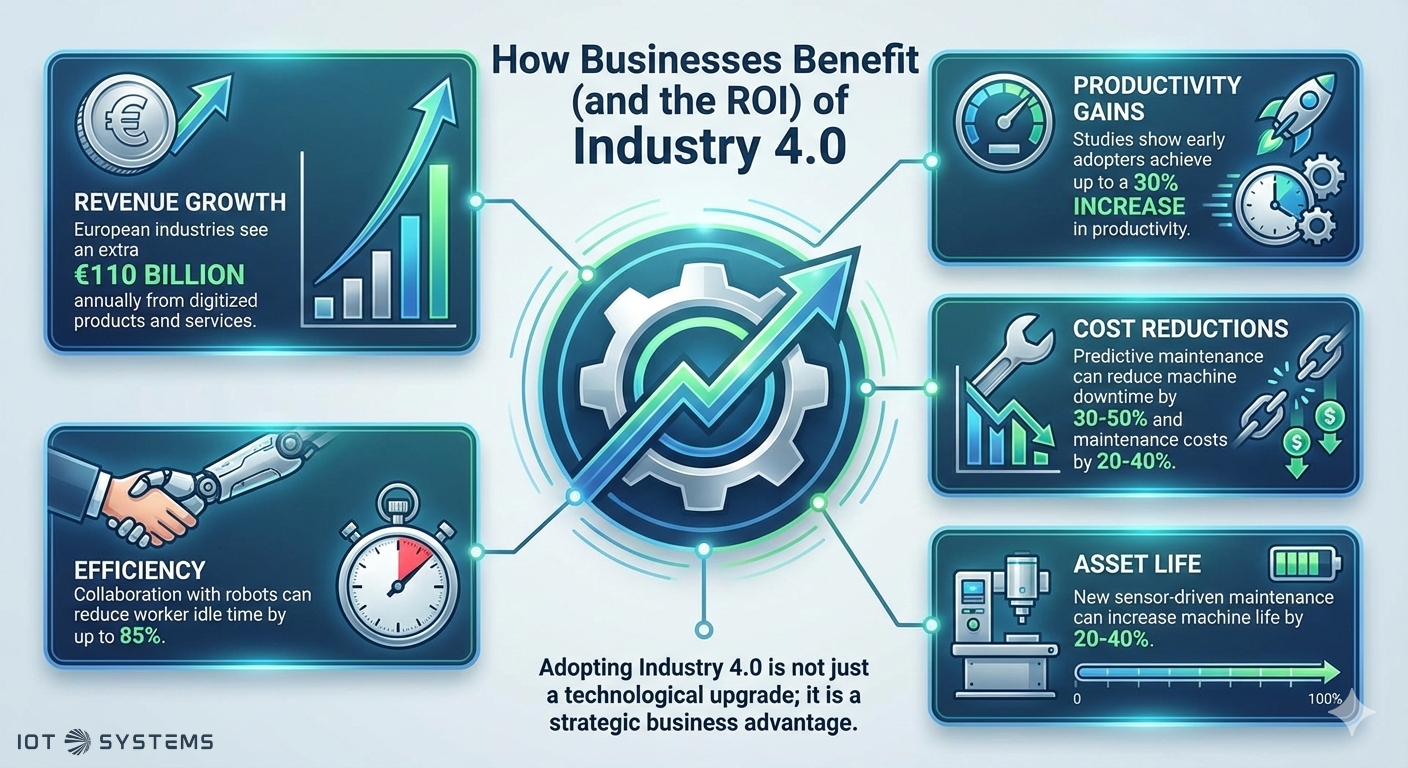
Adopting Industry 4.0 is not just a technological upgrade; it is a strategic business advantage.
• Revenue Growth: European industries see an extra €110 billion annually from digitized products and services.
• Productivity Gains: Studies show early adopters achieve up to a 30% increase in productivity.
• Cost Reductions: Predictive maintenance can reduce machine downtime by 30-50% and maintenance costs by 20-40%.
• Asset Life: New sensor-driven maintenance can increase machine life by 20-40%.
• Efficiency: Collaboration with robots can reduce worker idle time by up to 85%.
Common Challenges in Adopting Industry 4.0 and How to Overcome Them
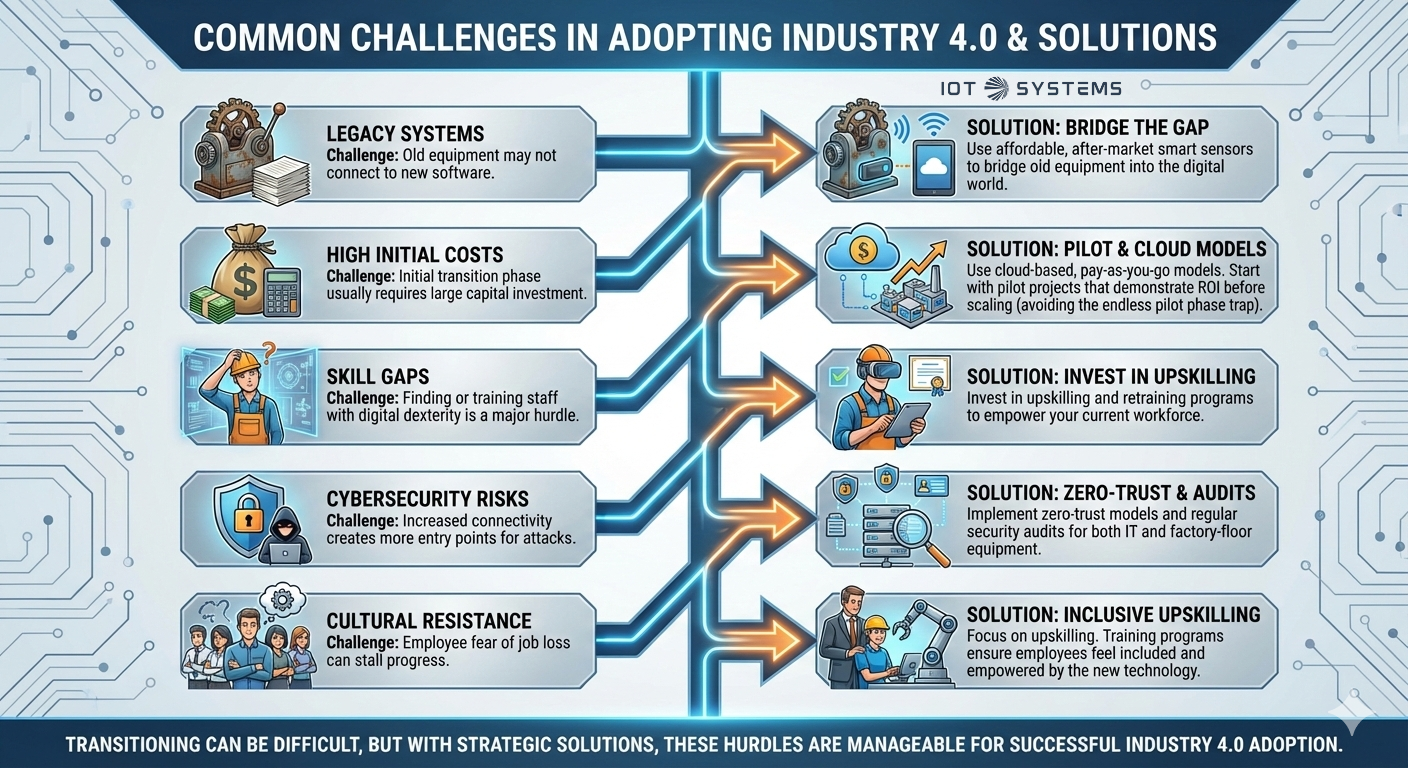
Transitioning can be difficult, but these hurdles can be managed:
- Legacy Systems: Old equipment may not connect to new software.
Solution: Use affordable, after-market smart sensors to bridge old equipment into the digital world. - High Initial Costs: Initial transition phase usually requires large capital investment.
Solution: Use cloud-based, pay-as-you-go models to minimize upfront capital investment. Start with pilot projects that demonstrate ROI before scaling (avoiding the endless pilot phase trap where projects never move beyond testing). - Skill Gaps: Finding or training staff with digital dexterity is a major hurdle.
Solution: Invest in upskilling and retraining programs to empower your current workforce.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity creates more entry points for attacks.
Solution: Implement zero-trust models and regular security audits for both IT and factory-floor equipment. - Cultural Resistance: Employee fear of job loss can stall progress.
Solution: Focus on upskilling. Training programs ensure employees feel included and empowered by the new technology.
Leading Companies and Countries Succeeding with Industry 4.0
Countries:
- Germany remains the benchmark with its national “Industrie 4.0” initiative.
- Singapore is a global leader in digital readiness and national workforce planning.
- China is prioritizing AI and robotics through its “Made in China 2025” plan.
Established Companies:
- Siemens’ Amberg factory uses IoT and AI to manage 16 million products annually. This connectivity allows them to track all product and process data in real-time, aiming for zero defects and enabling mass customization without losing efficiency.
- Tesla: Extensive robotics and AI assembly.
- Amazon: Robotics for warehouse picking.
- DHL: Machine learning for inventory optimization.
All these countries and companies are already reaping massive gains.
APAC Innovation Spotlight: Startups Driving Industry 4.0
The APAC region is home to a vibrant ecosystem of startups bringing Industry 4.0 solutions to diverse industries. These companies showcase how specialized technologies are making digital transformation accessible:
Smart Manufacturing & Quality Control:
- SixSense (Singapore): AI-powered visual inspection systems that detect defects and predict quality issues in real-time on factory floors, enabling predictive maintenance through advanced image recognition.
- WITTI Technology (Hong Kong): Smart Manufacturing Systems designed specifically for Greater Bay Area manufacturers, providing comprehensive digitalization solutions.
Industrial IoT Platforms:
- FAVORIOT (Malaysia): Malaysia’s leading IoT middleware platform with AI-powered analytics for predictive maintenance across smart cities, manufacturing, and agriculture sectors.
- HEXA IoT (Malaysia): Multi-sector IoT solutions for environmental monitoring, agriculture, and manufacturing. Recently showcased “Project A3”, an AI-integrated 5G remote-controlled all-terrain vehicle for tracking crop performance and improving harvests.
Advanced Automation & Robotics:
- ASA Robotics (Hong Kong): Vendor-independent robot fleet management platform allowing enterprises to control robots from different manufacturers through a single unified dashboard, solving the fragmentation problem of managing diverse robot fleets.
- DF Automation and Robotics (Malaysia): Complete factory automation systems for solar PV, electronics, and semiconductor industries.
Next-Gen Applications:
- Datakrew (Singapore): Real-time battery monitoring platform using IoT and AI to predict EV battery failures, optimize performance, and extend battery lifetime by analyzing BMS data, driving behavior, and road conditions.
- Polymerize (Singapore): Machine learning SaaS platform that predicts chemical formulations and material properties, reducing repetitive trial-and-error in R&D for chemical companies.
- Giant Technologies (Hong Kong): Develops ultra-wideband (UWB) chipsets with secure AES-128/256 encryption for robust IoT connectivity in industrial applications.
These startups demonstrate how Industry 4.0 technologies are being democratized and specialized across different sectors throughout the APAC region, making advanced solutions accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Can Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs) Benefit from Industry 4.0?
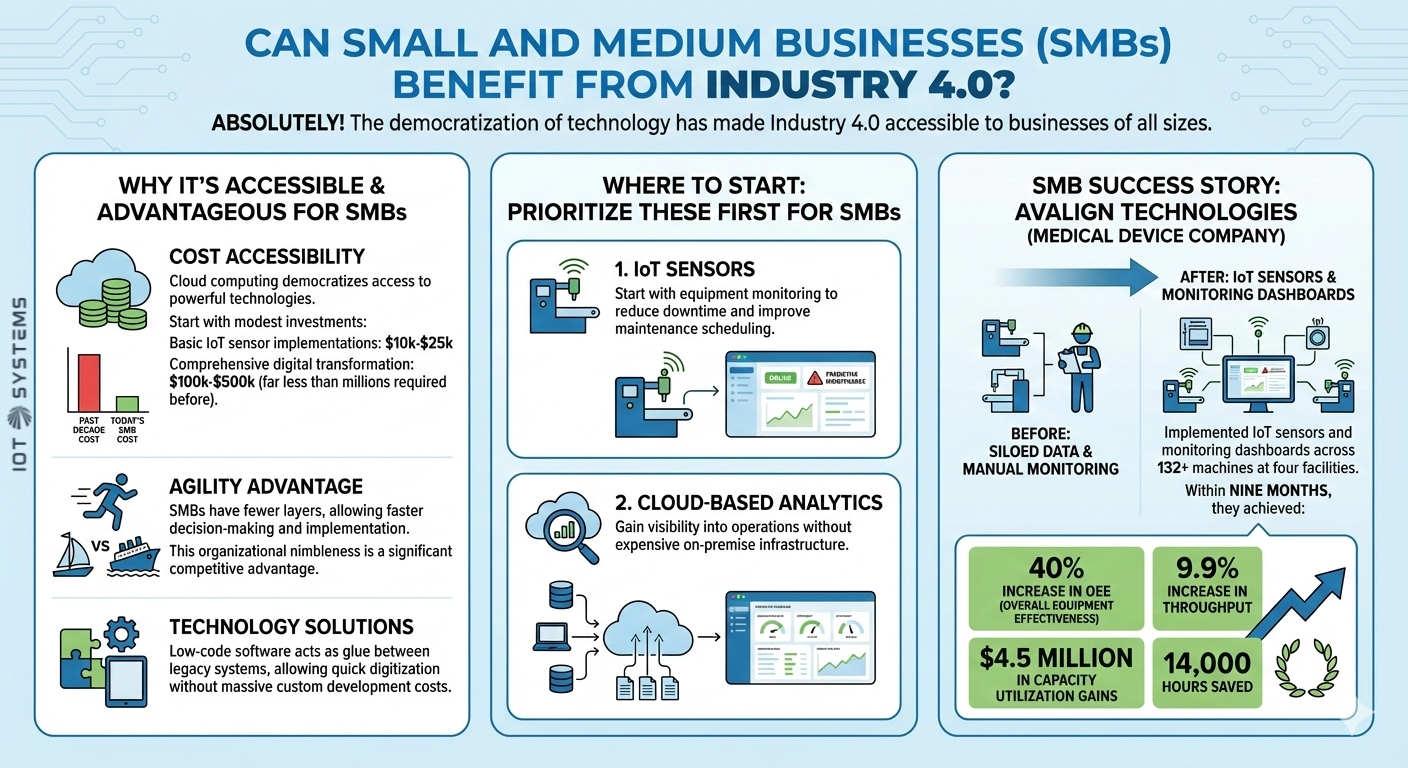
Absolutely! The democratization of technology has made Industry 4.0 accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Cost Accessibility: Cloud computing democratizes access to powerful technologies that were once only available to giant corporations. You can start with modest investments with basic IoT sensor implementations that can begin at $10,000-$25,000, while comprehensive digital transformation might range from $100,000-$500,000 depending on scale, far less than the millions required a decade ago.
Agility Advantage: SMBs have fewer layers, allowing them to make decisions and implement changes faster than large operations. This organizational nimbleness can be a significant competitive advantage.
Technology Solutions: Low-code software solutions can act as glue between legacy systems, allowing SMBs to digitize quickly without massive custom development costs.
Where to Start: For SMBs, prioritize these two technologies first:
- IoT Sensors: Start with equipment monitoring to reduce downtime and improve maintenance scheduling.
- Cloud-based Analytics: Gain visibility into your operations without investing in expensive on-premise infrastructure.
SMB Success Story: Avalign Technologies, a medical device company, implemented IoT sensors and monitoring dashboards across 132+ machines at four facilities. Within nine months, they achieved a 40% increase in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), 9.9% increase in throughput, $4.5 million in capacity utilization gains, and saved 14,000 hours.
Is Your Business Ready for Industry 4.0?
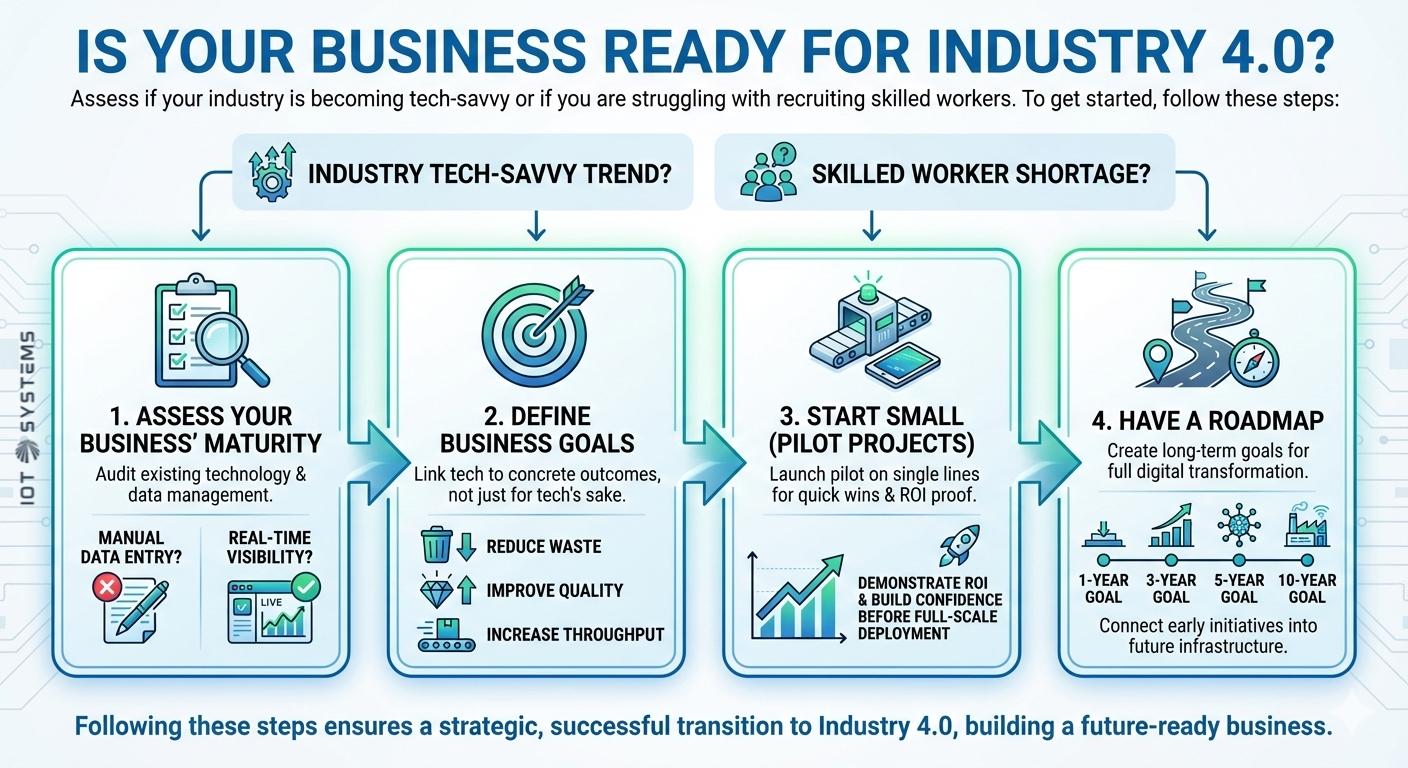
To determine if Industry 4.0 is right for you, assess if your industry is becoming tech-savvy or if you are struggling with recruiting skilled workers. To get started:
1. Assess Your Business’ Maturity: Audit your existing technology and data management processes. Are you still using manual data entry? Do you have visibility into real-time operations?
2. Define Business Goals: Don’t adopt tech for tech’s sake; link it to concrete outcomes like reducing waste, improving quality, or increasing throughput.
3. Start Small: Launch pilot projects on single lines to achieve quick wins that prove the concept. This approach demonstrates ROI and builds organizational confidence before full-scale deployment.
4. Have a Roadmap: Create 1, 3, 5, and 10-year goals to connect your early initiatives into a full digital transformation that will help build the infrastructure for later developments.
What’s Next? The Future and Industry 5.0
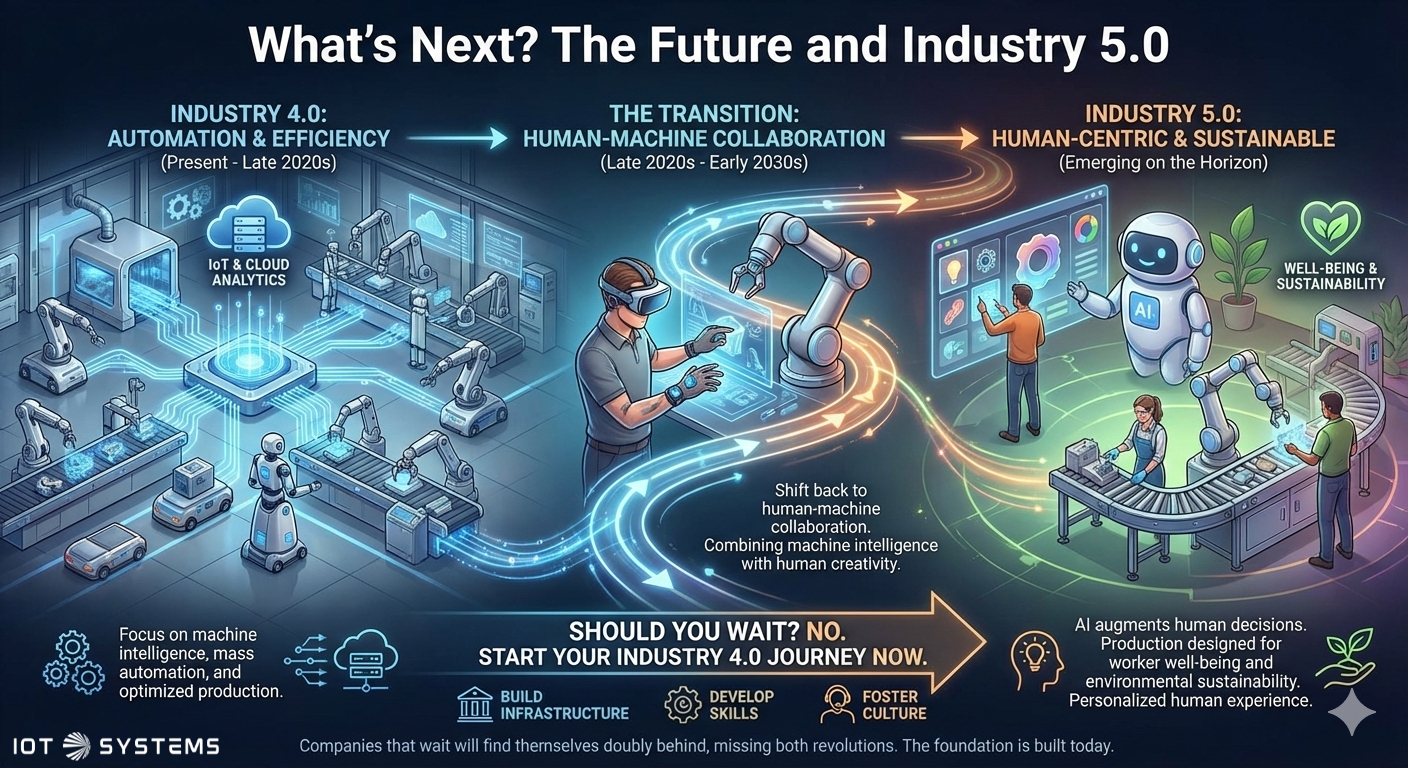
While Industry 4.0 focuses on automation and efficiency, Industry 5.0 is already emerging on the horizon (expected to mature in the late 2020s to early 2030s). It shifts the focus back to human-machine collaboration, aiming to combine machine intelligence with human creativity and adaptability. It seeks to create a more personalized and human experience for both workers and customers.
What Industry 5.0 looks like: Think collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside humans in creative tasks, AI systems that augment rather than replace human decision-making, and production systems designed around worker well-being and sustainability, not just efficiency.
Should you wait for 5.0? No. Start your Industry 4.0 journey now. The infrastructure, skills, and cultural changes you build today will form the foundation for Industry 5.0 adoption. Companies that wait will find themselves doubly behind, missing both revolutions.
Final Thoughts: Key Takeaways
- Industry 4.0 is about connected, autonomous systems that optimize production.
- The foundation is real-time data and hyperconnectivity.
- Starting small and focusing on ROI is the most effective way to avoid pilot purgatory (failing to scale into full production where projects never move beyond testing).
- The most successful transformations are people-focused, prioritizing culture and training over just technology.
- SMBs can absolutely benefit from Industry 4.0 with strategic, phased approaches.
Wondering where your business fits in the Industry 4.0 landscape? Book a free consultation with us to evaluate your current capabilities, identify quick wins, and build a roadmap tailored to your goals and budget.